In past modeling tips, we have discussed how to estimate sub-hourly pollutant concentrations using AERMOD, a Gaussian plume dispersion model with an hourly minimum time step. Now we look at how a similar concept can be modeled using a different modeling system – CALPUFF.
Modeling short-duration impacts is an important process in air dispersion modeling. Odors, for example, can occur over a short period of time where a one-hour (or longer) averaging period is not appropriate for detection. The CALPUFF Version 6 & Version 7 modeling systems support sub-hourly time steps allowing you to perform short-term modeling without using conversions during post-processing.
To run a sub-hourly modeling project using CALPUFF View, set the Time Step field in the CALMET and CALPUFF Run Information dialogs to the number of seconds desired. The example below uses a 600 second (10 minute) time step.
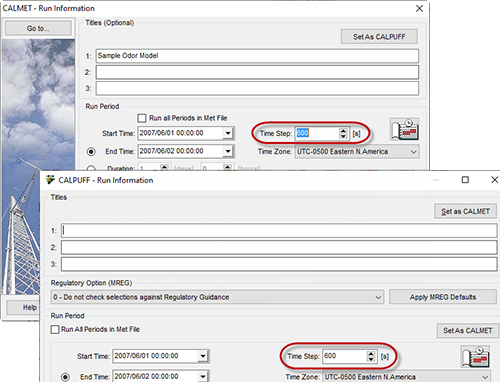
Input data to CALMET can be given in the assigned time step. If prognostic data are used as input, CALMET will interpolate the meteorological parameters to generate results in the user-defined time step.
After a successful model run, CALPUFF View’s Plume Animation will display the contours for each sub-hourly time step.
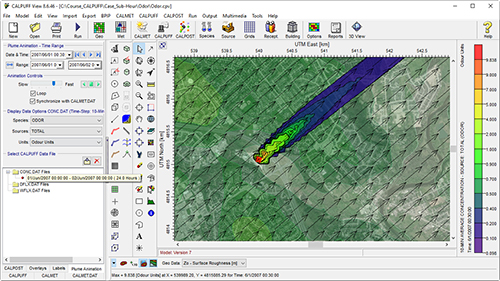
Sample project displaying instantaneous 10-minute average concentrations
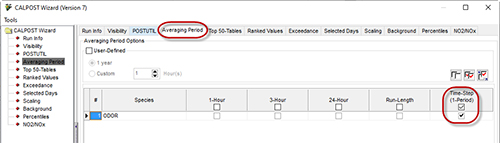
Sub-hourly averages can be calculated in CALPOST by selecting the Time-Step (1-Period) option within the Averaging Period tab of CALPUFF View’s CALPOST Options dialog.
|