|
When conducting an air dispersion modeling analysis with AERMOD, a common question arises as to what limits – if any – exist on where calculations can be performed by the model. Understanding the range of the model’s validity is important in interpreting results.
Minimum Distance
AERMOD has three primary checks when calculating the minimum distance between a source and receptor:
- Within 1 meter of POINT sources
- Within an exclusion zone of 1 meter + 2.15 * σY (initial lateral plume dimension) around a VOLUME source
- Inside the boundary of an OPENPIT
The volume source exclusion zone is based on the source’s effective radius estimated by multiplying the initial lateral plume dimension by 2.15. In AERMOD View, the exclusion zone can be plotted as a circular boundary around each volume.
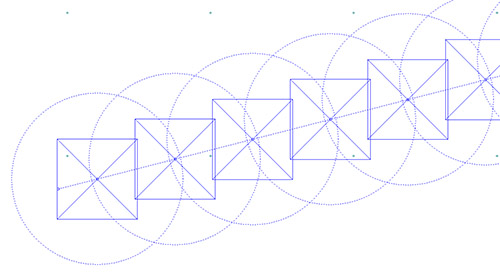
A series of volume sources with exclusion zones displayed
Maximum Distance
AERMOD places one limitation on maximum calculation distance – when the FASTALL or FASTAREA non-default model options are employed, the model limits calculations to within 80 kilometers of the source. For modeling done without FASTALL or FASTAREA, the model has no effective limit on maximum distance.
Caution is advised, however, as the model’s makeup as a steady-state plume model is best situated to performing calculations in the near field. Regulations in the United States, for example, only recommend use of AERMOD within 50 kilometers of the source. Care should be taken to ensure the model is employed in the proper manner.
The AERMOD output file prints a list of source-receptor combinations excluded from calculations. Modelers can review this file (*.ADO in AERMOD View) to confirm the exclusions.
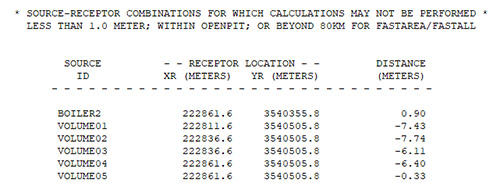
AERMOD Output File Example Listing Excluded Receptors
|