|
The Plume Volume Molar Ratio Method (PVMRM) is one of several methods built into AERMOD for assessing the conversion of NOX to NO2. Originally developed by Hanrahan as a post-processor for the ISCST3 model, this conversion method is considered a Tier 3 screening method according to the Guideline on Air Quality Models (Appendix W to 40 CFR Part 51). The conversion rate for NOX to NO2 in this scheme is based on a calculation of NOX moles emitted into the plume and the amount of ozone (O3) moles contained within the volume of the plume between the source and receptor.
When modeling PVMRM, users must supply in-stack NO2 / NOX ratios – which can be customized for each source – and background ozone concentrations. Background ozone values can vary from a single value representing the entire domain for the duration of the run to hourly values – like those taken from a monitor – which can vary by downwind sector.
In AERMOD View, background ozone values are input via the Control Pathway. To enable this feature, users must have the following options enabled:
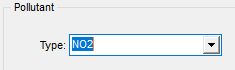
In Pollutant/Averaging, the pollutant Type to NO2
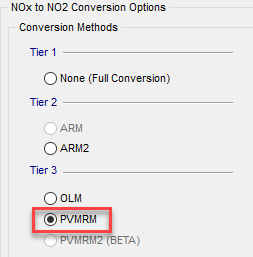
In NOx to NO2 Options, select PVMRM from the Tier 3 options
In addition to background ozone, users can also input background NO2 concentrations. These serve as additive values as additive values to the model-calculated concentrations and are input via the Source Pathway as shown below.
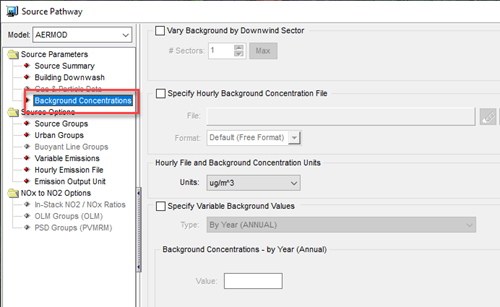
As with background ozone, these values can vary temporally – either hourly or by pre-defined repeating scales – and spatially by downwind sector.
The 21112 version of AERMOD published by the U.S. EPA on May 11, 2021 and incorporated in AERMOD View Version 10.0.1 contains a bug when reading background NO2 values from the Source Pathway. The bug causes background NO2 to be incorporated into the model calculations twice effectively doubling the amount of this background NO2 data.
The workaround is to input half of the actual background NO2 values. This way, the doubled background will work as the actual value.
The EPA plans to fix this issue in a future release of the AERMOD model.
As an example of the workaround, if your actual background NO2 was a single annual value of 30 µg/m3 you would input 15 µg/m3 using the “By Year (ANNUAL)” selection.
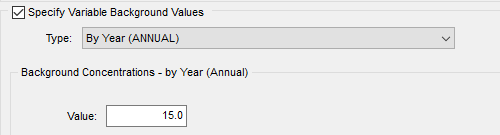
If you input hourly values using an Hourly Background Concentration File, each value must be halved. Note that you can build an hourly background data file using the Concentration File Maker utility.
The U.S. EPA has not released a timeline for fixing this issue, so modelers should take note of which projects they run containing reduced background ozone values. Whenever an updated AERMOD is available, Lakes will incorporate that into AERMOD View and advise on any further steps users need to take at that time.
|