|
AERMET – the meteorological pre-processor for the AERMOD modeling system – allows users to input their own custom meteorological data via its Onsite Pathway. This produces a highly representative dataset when using observations recorded at the site that will be modeled in AERMOD. One of the biggest challenges to this approach is that the modeler is responsible for identifying the variables and input format to AERMET. AERMET has two separate format specifications which can be utilized:
- FORTRAN statements, and
- FREE format
With FORTRAN statements, modelers tell AERMET the exact format of each line by defining each character (or ‘column’) as a certain character type. For example, I is reserved for integer values like date and time variables. Using a FORTRAN statement of I2 means a two-character integer variable will be read. F is used for floating values which have decimals, so a statement of F10.2 means a numeric value with 10 characters (including the decimal point) and 2 characters that appear after the decimal.
FREE format – also called list-directed data – is read as a list of values which are separated by at least one blank space or a comma. Using this option greatly simplifies the process of identifying the file format structure but requires every single data value be read into AERMET (i.e., you cannot skip any values).
In AERMET View, formatting inputs are specified on the Data Records tab of the Onsite Pathway. The image below shows an example file which is read using the FORTRAN Format option. Since no values were skipped in this observation, the FREE format option could have also been used to produce the same result from AERMET.
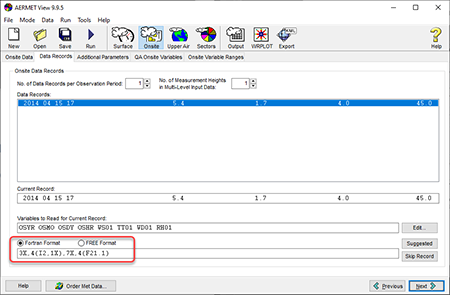
Using FORTRAN statements can be a challenge for modelers not familiar with the FORTRAN language, AERMET View includes a  button which will read the line of data and come up with a suggested FORTRAN statement. button which will read the line of data and come up with a suggested FORTRAN statement.
Next month, we’ll take a closer look at rules and guidelines for formatting your Onsite data file.
|