|
With the latest release of the AERMOD model dated 22112, the U.S. EPA has continued to expand the formulated capabilities of the model. Most of these updates have been added as ALPHA non-default options, a concept we covered in a previous modeling tip. AERMOD 22112 contains 6 new ALPHA options which are described below:
Platform Downwash
Taken from the Offshore and Coastal Dispersion Model (OCD), the U.S. EPA’s preferred model for calculating near-field air pollutant impacts from overwater emission sources, platform downwash algorithms have been integrated into AERMOD for point, horizontal point, and capped point sources.
After identifying the source – with the source’s height identified as the height above sea surface – the platform is identified with the following parameters:
- Zelp: Height of the platform bottom above sea surface
- Hb: Total height (above sea surface) of the tallest solid or “influential” building
- Wb: The lesser width of buildings that can influence downwash when comparing side and end views of the platform (see the image below)
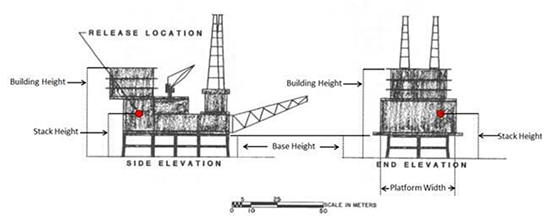
Platform downwash as considered by AERMOD 22112 (taken from U.S. EPA AERMOD User’s Guide [2022]).
TTRM2 NO2 Conversion Method
The Travel Time Reaction Method (TTRM) was first implemented as a stand-alone ALPHA option in AERMOD 21112. The new TTRM2 option was integrated to allow the model to assess TTRM simultaneously with existing NO2 conversion methods (PVMRM, OLM, & ARM2).
When TTRM2 is selected along with one of the other NO2 conversion methods, TTRM will be implemented for near-field receptors where the fraction of conversion remains below the upper limit of the equilibrium fraction (usually 0.90). For all other receptors, the other specific method is used.
Sidewash Point Source
This new specialized point source type was developed to further study the effect of the lateral shift of the building wake cavity that forms when the wind is oblique to one of the longer sides of an elongated building.
Unlike traditional point sources, sidewash points are defined by their location, height, emissions, and the dimensions of the rectangular building that will influence flow (width, length, and compass angle). This source is designed to only calculate concentrations within the building wake cavity, and it does not consider terrain, traditional plume rise (i.e., momentum vs. buoyancy), and PRIME downwash is not applied.
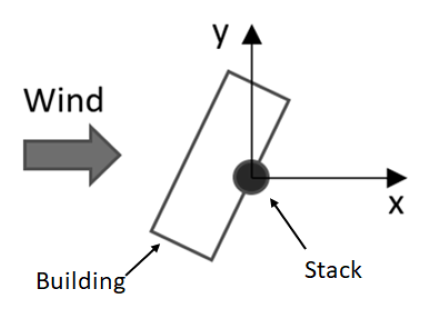
Depiction of SWPOINT Source from U.S. EPA AERMOD User’s Guide (2022)
RLINE Wind Speed Profile
This option (RLINEFDH) removes the displacement height used in the RLINE source algorithm for calculating the wind profile near the surface. With this option implemented, the wind speed profile is calculated similar to other AERMOD source types.
Low Wind Options
Two additional options have been added to the existing LOW_WIND keyword:
- FRANmin – A minimum value for the plume meander factor. Users could already restrict the maximum meander factor (FRANmax), and now they can control the minimum factor.
- PBAL – Overrides the default energy balance approach for plume meander to an alternate momentum balance approach.
AWMA Downwash Updates
For the AWMAUTURB & AWMAUTURBHX options, internal limits were modified (tiz from 50 to 18, tiy from 50 to 6).
Lakes Environmental’s development team is hard at work incorporating these new features into the AERMOD View application. A new version will be ready soon so users can begin testing and evaluating these new model options.
|
